Current
06 Dec 2021
Blockchain and its future with Digital Transformation
Let’s look at the new fad that has its roots all the way back in 1991, and how it is affecting the future of Digital Transformation (DX)! Blockchain and all that makes it work, is it a fad that we’ll forget in a couple of years or is it really the bright future that some people will swear it is!
With 2022 breathing down our necks, we can’t help ourselves and stay hopeful! No, we’re obviously not talking about the COVID-19 pandemic, and the newly discovered Omicron variant. If anything, things seem to be steadily going downhill on that front.

However, the future for software never seemed brighter! With growing need for a greater number of custom solutions for various day-to-day activities that moved from the outside into the comfort of our homes; we’re just happy we’re right in the middle of pathing this future with the rest of software development world!
And one of those shining examples of innovation is Blockchain technology! But there seems to be a lot of misunderstanding behind this term, especially with marketing efforts trying to introduce this term “into the masses”!
These misunderstandings lead many to a situation when they hear someone say blockchain, their mind instantly goes to – Bitcoin/Cryptocurrency. And they’re not entirely wrong, but as always, that is merely a part of the picture. So, today our goal is to lift the veil on the rest of the picture and give you an overview of blockchain technology, its roots, its goals, and mostly importantly where is it all going!
Where does blockchain come from?
There is a good reason why many people hear “Cryptocurrency” when you tell them blockchain, for those two things are heavily interlinked. The technology that essentially allows cryptocurrencies to exist, is called “blockchain” and the very first instance of it being used in the real world was Bitcoin in 2009.
But the actual story roots back to 1991. It all begins at “Bellcore Labs” credited with many advancements in the field of computer science and telecommunications, like C Programming language, or OS – Unix among other things. But we digress.
Two engineers named Stuart Haber and Scott Stornetta, were give full freedom in choosing which projects they want to work on. The one they had their sights on was digital document authentication: How can you make sure you’re looking at an original unaltered document?
After numerous discussions, they seemed to always come up with the same problem – You need a third body/independent party to verify the file, but what they were also “in on it”? It might seem simple – just add an extra authenticator. Well, what if they are also in cahoots? This process could continue indefinitely until you ended up with the whole world as the voucher for someone in the system.
What they finally decided on is to create a form of a time-fingerprint of a file, and called it timestamp certificate. A separate system creating files out of hash functions and making a “fingerprint” of a certain document in its current form, and then storing it on a separate system for later validation. Because its custom encrypted, there’s no way to tamper with it.
Of course, it wasn’t until 2009 when Bitcoin used this technology to create its cryptocurrency, now days we call it a Distributed Ledger Technology, or more commonly referred to as Blockchain.
(DLT) Distributed Ledger Technology – what and how?
DLT or Distributed Ledger Technology is the catch all term for the complex infrastructure and protocols involved in accessing, validation, and introducing new data into a immutable manner across a massive shared network spread over multiple entities and locations.
The name of the game is decentralization, which by default makes us all jump with excitement, after all, we’re big supporters of decentralized, decoupled infrastructures!
But anyway, DLT/blockchain is a protocol governing secure functionality over a large network of digital databases. What that means, it’s write once, open indefinitely and its as secure as if you were to chisel your information in cement for it is as state – immutable. The bigger the network, the more secure it gets.
Essentially this Ledger is a massive number of different computers, or better said data storages, each holding the encrypted digital database in question, and each keeping an eye on each other.
Those more astute of you will naturally ask yourself – but what makes this different from a cloud service database? Don’t they also have massive servers all over the world usually keeping the same data for recovery purposes?
Cloud vs Blockchain, why is it even called that?
The key difference is the way the data is stored, we’ve mentioned the time sensitive fingerprint, which the technology is based on.
Well, essentially the data is stored in chunks, or blocks, and it’s added similarly, in a chronological order. Each block contains encrypted hashes describing its neighbouring block.
The database is built in such a way that the data you’re storing also contains encrypted instructions on what it expects to see in its neighbour.
These instructions form a chain link between each block of data, hence blockchain.
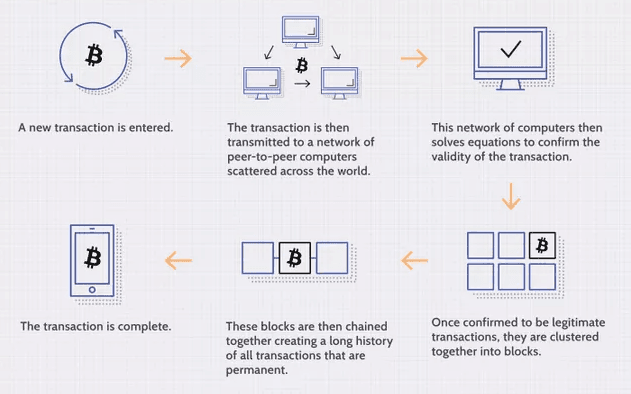
It can only be added upon, not edited… well it can be edited as any form of digital information, but it will require that at least 51% of the network agree on the change.
And even then it wouldn’t be “changing” or “altering” it, but merely creating a new branch. Such as what happened with Ethereum. A crypto-skism if you will…
And the bigger the ledger, the more daunting this task is to perform.
If a bad actor of any type (be a hacker, disgruntled employee, or human error) decides to alter the records in any way, it would have to attack the whole network at the same time.
At the end of the day – Blockchain or DTL is simply a form of storing data.
Blockchain is perfect for the Finance sector
In Bitcoins instance, there is no central authority governing or controlling the value or availability of coins.
Everyone holds a node; everyone maintains this network and keeps it in check. If one node shows wrong information, the rest of the network simply marks that node as false and moves on.
This is precisely why blockchain technology sees such massive success in cryptocurrency and financial sector.
Because it relies on a massive network of devices, localised outages, natural disasters or other ”downtime cost” related issues never affect Blockchain built databases!
Unlike typical centralized SQL databases (used in big bank networks for instance) blockchain databases are not controlled by any one entity, but rather all and no one at the same time. So, no one can simply “edit” money into their account because it would instantly discredit that node as false within the network.
They can attempt to “fudge” the hash codes within a block they desire and make a (single) node believe the information, however it would be instantly identified as false due to discrepancy between the instructions of its neighbours. And if attempting to change those as well, well their neighbours will be affected etc etc.
Everyone has access to the same ledger and database; they can see all the transactions ever performed. And because it’s immutable, all the history of transactions as well which cannot be altered, deleted or destroyed!
All this allows for greater transparency as well higher degree of security.
How does Blockchain affect Digital Transformation?
Alright but how does it affect Digital Transformation efforts? Well, as we’ve mentioned blockchain is merely a “way” of storing and building databases. So essentially anything that needs a database of information of any sort, benefits from this technology.
Because there is no central entity that holds the reins, rather everyone does, it makes is much better alternative in home/property ownership, product/item inventory tracking, even improving government/state electoral systems and many other different needs.
So regardless of the market you’re in, if you have any form of information that needs a secure and most importantly trusted form of storage – then blockchain technology is going to be within your sights now, while everyone is adapting it, or later when everyone already has, and you’re lagging behind.
Everyone knows that speed is among the leading deciding factors whether your business succeeds or fails. And much like Edge computing, DTL built infrastructure is much more reliable and faster than typical data centric systems. Your users/customers will automatically receive their data from the closest node within the network, rather than connecting to possibly far away built datacentres and suffering latency or bottleneck issues.
Or think of the massive food industry supply chains involved in brining food onto your plate each day. Then remember all the e.coli or norovirus outbreaks involved due to poor sanitation during transportation of goods. Using blockchain based databases everyone will have access to the supply network and all its steps. Hence tracing exactly what steps and when were taken is incredibly beneficial in tracking those avoiding regulations.
The key benefit of the technology still remains the absolute trust of everyone involved in the system, it is literally un-tamper-able: transactions, supply chains, deeds etc.
Smart Contracts – Blockchain
Blockchain networks are basically data environments that are immutable to all, and as any environment you can code within it. With limits of course. Because everything is set up linearly and chronologically you can set up a clear and agreed upon all if/when/else/then etc statements that auto fulfil and up into the chain the progression of tasks. Essentially allowing you to code your contracts or business processes, which again, are available to be viewed by everyone with proper keys, but not change.
A network of computers within the blockchain adds new blocks when a set of predefined conditions have been met and verified by all parties. These can be automatic payments, registration of wares, notifications, tickets etc.
As any software you can make these as complex as your business and interested parties’ desire. Then mutually agreeing to the contract, it essentially binds everyone until full completion and all the conditions have been met. This sort of binding can and is incredibly useful in the B2C and B2B sphere.
Farewell
But that’s all: we have a basic overview on what blockchain technology is. This topic as many that we tackle here on our blog, is incredibly complex and difficult. So, we’ve just scratched the absolute surface of the issue. Be sure however, that we’ll be returning to this topic multiple times in the following year. Afterall, US alone is planning to spend $4.2 billion in 2022 on DTL technologies, this is comparing to its $1.1 billion in 2019.
So, you can be sure that Blockchain is not going anywhere, anytime soon. And it is genuinely the solution many in the world were looking for to solve their security and trust issues for many years.

But what do you think about this technology? Do you think it does solve the security and trust issues as everyone seems to claim, or is it simply a fad bubble that will burst in the near future? Tell us in the comments!
Stay classy business and tech nerds!
Share this article on:
Sign up for our
newsletter.
Be up-to-date with our latest news, in-depth insights, and privileged content.

Data Analytics
Data engineering
Technology
2018 is becoming quite promising for augmented reality (AR) and this goes way beyond Pokemon Go. AR is changing the world of consumer marketing. It empowers stakeholders and clients to experience products and services as “prescribed”. It acts as “a sibling” to Virtual Reality platforms aiding physical reality with virtual objects. This way AR is delivering a new, interactive customer experience. Unlike other hypes we’ve seen rising, this tech is here to stay with figures expected to reach $117.4 billion by 2022.
12 Feb 2018

Data engineering
Data Analytics
Peeling this BASICs digital onion, we’ve left some details out (particularly in our last article). As stated, data-centric and data-driven applications deserve their series, a journey we’re kicking off today. Before talking about BigData, strategies and mechanics, let’s filter the messy data-centric vs data-driven dilemma.
24 Aug 2020